How to Choose and Use Sunscreen
Finding the right sunscreen is essential for protecting your skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Here, we’ll guide you through the important points to consider when selecting a sunscreen and how to use it effectively.
Understanding SPF
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) measures a sunscreen’s ability to prevent UVB rays from damaging the skin. UVB rays are responsible for sunburn and contribute to skin cancer. The number indicates how long you can stay in the sun without burning while using the sunscreen compared to without it. For example, an SPF 30 product protects you 30 times longer. Generally, dermatologists recommend using a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, which blocks about 97% of UVB rays. Higher SPF numbers (50+) offer slightly more protection but aren’t significantly higher and can give a false sense of security.
Broad-Spectrum Protection
Look for labels that state “broad-spectrum” protection. Broad-spectrum sunscreen shields you from both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are responsible for premature aging and can contribute to skin cancer. A broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential for comprehensive protection against both types of UV radiation.
Types of Sunscreen
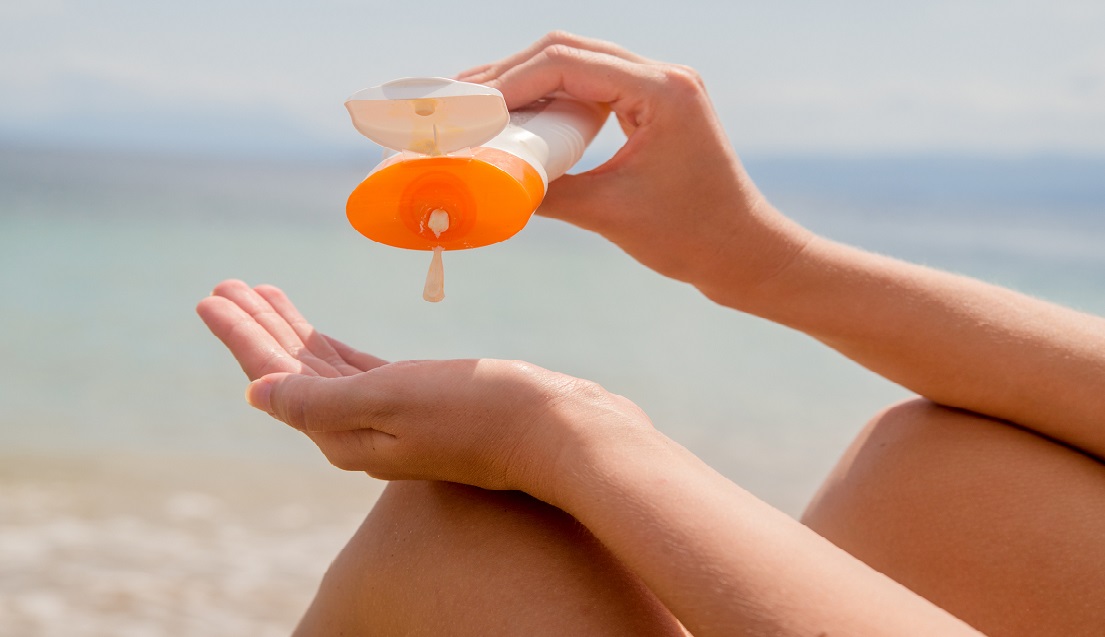
Sunscreens come in various formulations, including lotions, creams, gels, sprays, and sticks. Each form has its own benefits based on individual preferences and skin types:
- Lotions and Creams: These are suitable for dry skin and larger area applications, like the legs and arms. Creams can also be beneficial for the face.
- Gels: Ideal for hairy areas, such as the scalp or chest.
- Sprays: Convenient for quick application and reapplication, especially on children. However, ensure good ventilation to avoid inhaling the spray.
- Stick Sunscreens: Handy for applying around the eyes and on the lips.
Consider your lifestyle and the conditions under which you’ll need to use sunscreen to choose the best type for you.
Ingredients to Look For
Common active ingredients in sunscreens include:
- Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide: Mineral-based ingredients that sit on the skin’s surface and reflect UV rays. Perfect for sensitive skin.
- Avobenzone, Octocrylene, Oxybenzone: Chemical filters that absorb UV radiation. These can be more suitable for oily skin types.
Check for water-resistant properties if you plan on swimming or sweating. Water-resistant sunscreens maintain their SPF for up to 40 or 80 minutes while in water.
For Various Skin Types and Conditions
Customization for different skin types is essential:
- Sensitive Skin: Opt for mineral sunscreens (zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) to reduce irritation. Fragrance-free and hypoallergenic formulas are best.
- Oily or Acne-Prone Skin: Choose non-comedogenic and oil-free options to prevent clogged pores.
- Dry Skin: Cream-based sunscreens enriched with hydrating ingredients like glycerin or hyaluronic acid work well.
- Children’s Skin: Pediatricians recommend mineral sunscreens for children under six months. Older children often need formulations that are gentle and easy to apply.
Application Tips
Proper application is vital for effective protection:
- Amount: Adults should use about one ounce (enough to fill a shot glass) for full-body coverage. Apply generously to all exposed skin.
- Timing: Apply sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors to allow absorption. Reapply at least every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
- Technique: Use even strokes to apply. Don’t forget easily missed areas such as the ears, back of the neck, tops of feet, and the part in your hair. Stick sunscreen around sensitive areas like the eyes and lips to avoid stinging.
Combining Sunscreen with Other Protective Measures
While sunscreen is crucial, it’s most effective when combined with other sun protection strategies:
- Clothing: Wear long sleeves, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-protective sunglasses to shield as much skin as possible.
- Shade: Seek shade during peak sun intensity hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Sunscreen with Makeup: Sunscreen should be the last step of your skincare routine, but before applying foundation or makeup. Consider purchasing makeup with added SPF for extra insurance.
Common Myths Busted
There are several misconceptions about sunscreen usage:
- Myth #1: Dark Skin Doesn’t Need Sunscreen: Even though darker skin has more melanin, which offers some protection, it still needs sunscreen to protect against UV damage and skin cancer.
- Myth #2: Sunscreen Causes Vitamin D Deficiency: Using sunscreen wouldn’t hinder vitamin D production significantly. A short daily exposure without sunscreen, around 15 minutes, is usually sufficient for most people.
- Myth #3: Sunscreen Use is Only Necessary at the Beach: UV rays penetrate through clouds and can reflect off surfaces like snow and cement. Daily use is important, even in winter or cloudy conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Some sunscreen ingredients have environmental impacts, especially on marine life. From 2021, the U.S. banned sunscreens containing oxybenzone and octinoxate in Hawaii due to their harmful effects on coral reefs. Consider choosing reef-safe sunscreens, typically mineral-based products, if you plan to swim in natural bodies of water.
Checking for Expiry
Sunscreen loses its effectiveness over time, so it’s important to check expiration dates on the packaging. Most sunscreens have a shelf life of about three years. If in doubt or if the texture and smell seem off, replace your sunscreen.
Final Thoughts
Choosing and using the right sunscreen involves understanding your skin type, selecting appropriate formulations, and following best practices to ensure optimal protection. Incorporate sunscreen into your daily routine regardless of the weather or season and combine it with other protective measures for comprehensive sun safety. By staying informed and making mindful choices, you boost your defense against harmful UV radiation and maintain healthier skin in the long run.