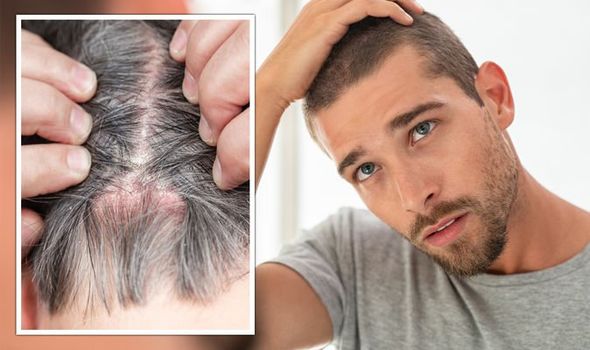
Itchy, scaly skin patches don’t just come to be carried around, especially when they last or become persistent. Treatment for psoriasis and fungal infections is: medicated shampoos, OTC meds, and prescription topical products. In adults, psoriasis is often mistaken for a fungal infection because its visual symptoms can look very similar. But they were totally different in cause and in treatment. If you do not know what’s going on with your skin, we will explain the main differences between psoriasis vs fungal infection.
Is It Psoriasis or a Fungal Infection?
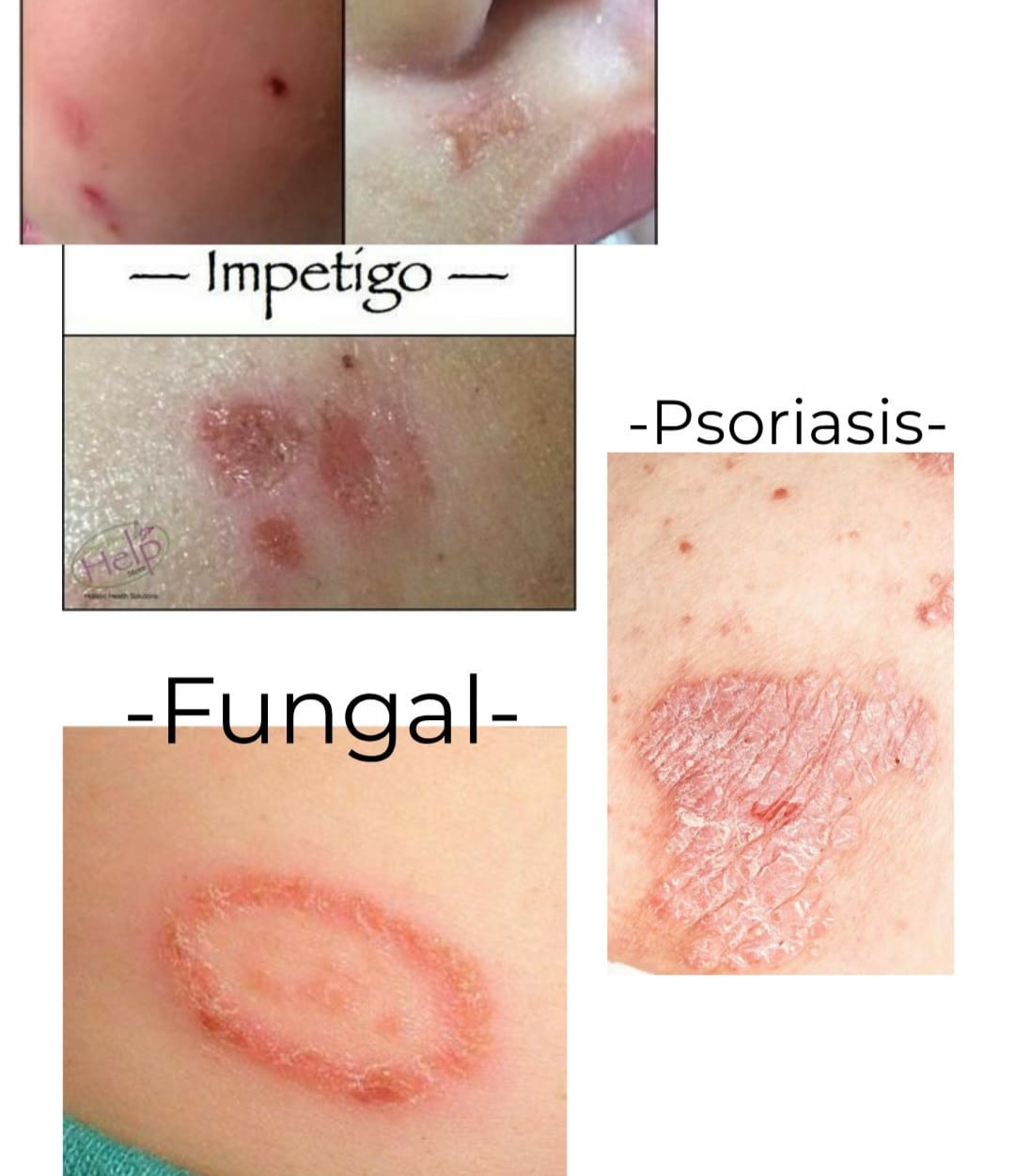
If you’re seeing red, itchy patches on your skin, determining whether it’s psoriasis or a fungal infection isn’t always straightforward. Look closely at the red patches: if they appear silvery, it’s likely psoriasis; if they resemble circles or rings, it’s more probable to be a fungal infection. [2]
What is Psoriasis?
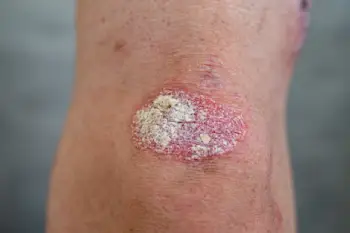
Psoriasis is a non-contagious habitual chronic skin condition that results from an overactive immune response.
Plaque psoriasis is the form most people hear about first, mostly because it shows up when skin renews itself far quicker than it should. The cells don’t shed evenly; instead, they build up and form thicker patches with a pale, silvery layer on top and edges that look mildly irritated. These psoriatic lesions often settle on the elbows, knees, scalp, back, or even around the nails. A flare may start after stress, an infection, a small injury to the skin, or certain medicines, and for many people it begins quite suddenly, without any clear cause.
The disease can wax and wane, sometimes receding for periods of calm before flaring up dramatically. Psoriasis is not an infection and therefore does not spread either severely or to another person. It may be triggered by many things and may manifest entirely over the skin, making life rough both physically and emotionally.
Is Psoriasis a Fungus?
Psoriasis is not caused by a fungus. It’s an autoimmune condition where the immune system triggers rapid skin cell growth, resulting in thick, red patches with silvery scales.
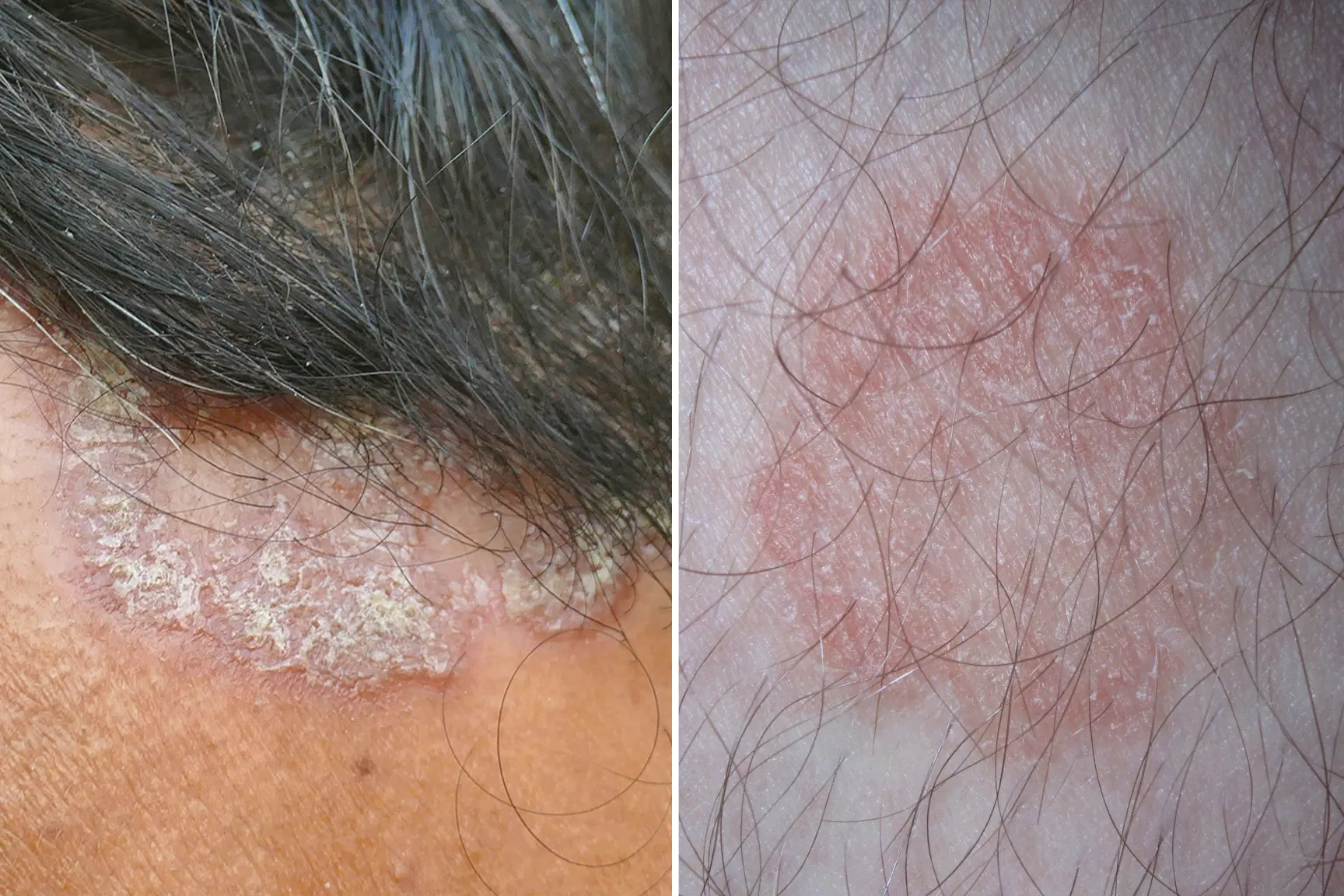
What is a Fungal Infection?

Ringworm. Getty Images/phanasitti
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis or fungal disease, is a type of disease caused by numerous kinds of fungi, yeasts, and molds.
Fungi mostly infect the skin or the nails, but other possible areas include parts of the mouth, lungs, and throat, even reaching the urinary tract. [4]
Common fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, nail fungus (onychomycosis), and oral thrush (candidiasis).
Signs and Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Plaque: Raised, reddish skin patches
- Silvery Scales: Thick, dry patches often have a white covering of scales.
- Itchy, Cracked Skin: It may itch and crack, sometimes leading to bleeding.
- Nail changes: Pitting, discoloration, or thickening of nails. [5]
- Inflammation: Redness and swelling in affected areas
- Koebner Phenomenon: New patches may develop at sites of skin trauma or injury
Signs and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
- Redness
- Itching and stinging in the affected area
- Circular or ring-like rash
- The skin may develop scales or flakiness.
- Discoloration and blisters on the affected area [6]
- Cracking or peeling of the skin
- Small bumps, patches, or raised areas
- Unpleasant odor
- Nail Involvement
Psoriasis Risk Factors
While doctors haven’t pinpointed the exact cause of psoriasis, genetics are known to be a factor.
Other risk factors or factors that can aggravate psoriasis include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Cold or dry air
- Various environmental factors
- Chronic or severe stress
Difference Between Psoriasis and Fungal Infection – An Overview
|
Aspect |
Psoriasis |
Fungal Infection |
|
Cause |
Chronic autoimmune condition |
Caused by various types of fungi |
|
Genetic Predisposition |
Common, tends to run in families |
Not typically associated with genetics |
|
Triggers |
Stress, infections, injury to the skin, certain medications |
Often related to warm, moist environments, contact with fungi |
|
Locations |
Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, nails, can appear anywhere |
Warm, moist areas like feet, groin, scalp, nails |
|
Contagious |
Not contagious |
Contagious, can spread from person to person or via surfaces |
|
Symptoms |
Red, raised patches with silvery scales, may itch. |
Redness, itching, scaling, sometimes blisters or oozing, may have characteristic appearances (e.g., ringworm) |
|
Treatment |
Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications |
Antifungal medications (topical creams, oral medications, shampoos, nail lacquers) |
What are the Causes of Psoriasis and Fungal Infections?

Knowing about psoriasis and fungal infections isn’t sufficient without understanding their causes. Let’s examine the causes of each condition separately.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Various fungi cause fungal infections, each leading to specific types of infections.
- Dermatophytes, responsible for ringworm and athlete’s foot, infect the skin’s keratin layer.
- Yeast infections, like those caused by Candida species, occur due to skin barrier disruption or environmental changes.
- Different types of fungi can cause these fungal infections, and they’re often superficial, affecting the hair, skin, nails, or any area in contact with the fungus.
Fungal infections spread easily through contact, such as:
- Direct contact with infected individuals
- Contact with animals carrying fungal infections
- Interaction with unwashed items like toys, floors, or clothes
- Exposure to contaminated surfaces like public pools or bathrooms
Causes of Psoriasis
The cause of psoriasis isn’t entirely clear but likely involves genetics, environment, and immune system factors.
- Genetics: Family history and genetic variations increase the risk. Specific genes, like HLA-Cw6, increase susceptibility. [7]
- Immune system dysfunction: Autoimmune response attacks healthy skin cells. T cells release cytokines, causing inflammation.
- Environmental triggers: Stress, infections, skin injury, smoking, and certain medications.
- Rapid Keratinocyte Proliferation: Abnormal activation prompts quick skin cell growth.
- Lifestyle factors: Obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol, poor diet.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis and Fungal Infections
Your dermatologist or doctor will base the diagnosis on what is seen but may need tests to be done in order to confirm the cause of the nail problem.
Nail Psoriasis VS Fungus
Although both cause the nails to appear thick, yellowish, or brittle, they differ. Toenails affected by psoriasis: Most individuals affected by nail psoriasis have pitting (little indentations on the nails). It can also harm the surrounding structures of the nails, such as the cuticles. Their nails may also become rough, thickened, or oil-drop nails. Finger or toenail fungus can cause the nail to darken, crumble at the ends, and sometimes lift away from the bed. While fungal infections come from microorganisms, psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder caused by immune system failure.
Nail Psoriasis
- Testing the nail through a biopsy or analyzing nail clippings can help confirm psoriasis. [8]
- Your healthcare provider will also check for plaques or lesions on other parts of your body.
- Sometimes, dermoscopy, a close dermatoscopic examination, may be used.
Nail Fungus
- Scraping or clipping is taken for testing either to confirm nail fungus or to identify the organism causing the infection.
- Lab tests of skin or nail particles can pinpoint the exact fungi causing the issue and guide treatment.
Psoriasis Treatments
The goal of treating psoriasis is to lessen inflammation, slow down skin cell growth, and ease symptoms. While there’s no cure yet, various treatments can help manage the condition.
Your doctor may recommend:
- Topical creams such as coal tar extracts
- Narrow band ultraviolet (UVB) light therapy [10]
- Topical Retinoids
- Topical Vitamin D analogues
- Oral medications
- Biologic injections
- Topical Corticosteroids [9]
Treatments for Fungal Infections
Fungal infections often respond well to topical antifungal creams or oral tablets, some available over the counter. [11] If these infections persist, your doctor might recommend changes in hygiene habits.
Treatment focuses on eliminating the underlying fungus through:
- Hygiene Adjustments
- Topical and Oral Antifungals
- Nail removal, if necessary
- Antifungal Shampoos
When to See a Doctor
If your itching persists without diagnosis or worsens, it’s best to contact a doctor. Also, seek a stronger prescription if an over-the-counter treatment isn’t effective.
Since these conditions appear similar, your doctor may need more than a visual inspection to determine the cause. In such cases, a biopsy may be necessary to identify the underlying issue and facilitate appropriate treatment.
Summary
Psoriasis vs fungal infection both cause enduring damage to your skin and nails, but they operate through entirely different biological processes since psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, while fungal infections stem from contagious agents. The treatments for these conditions exist, but psoriasis remains an eternal disease that cannot be cured. The essential factor requires an appropriate diagnosis to receive precise treatment. If you are experiencing persistent, spreading, or changing symptoms, book a dermatology consultation.