Harmful Habits Linked to Skin Diseases
Why is my skin so bad? Often, it’s due to common harmful habits. Bad routines like neglecting proper skincare can lead to various skin conditions. For instance, not removing makeup can clog your pores, while irregular washing and moisturizing can leave your skin vulnerable to environmental damage. The American Academy of Dermatology (2021) reports that failing to wash your face daily can lead to a significant increase in acne breakouts. Additionally, using products not suited for your skin type can exacerbate skin issues. It’s essential to understand what is bad for your skin and modify these habits to maintain a healthy complexion. Remember, skincare isn’t just about products; it’s about lifestyle choices too.
The Impact of Poor Hygiene on Skin Health
Poor hygiene is a major factor contributing to bad facial skin and other skin issues. Neglecting regular cleansing can lead to the buildup of dirt, oil, and bacteria, which can exacerbate skin problems. A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Science (2020) found that inadequate facial hygiene was significantly associated with the development of acne. Dermatologists emphasize the importance of a consistent hygiene routine, including washing your face twice daily, to keep your skin in good condition. Remember, your skin is a reflection of your overall health, and maintaining cleanliness is key to a radiant complexion.
Dietary Habits and Skin Health
What we eat significantly affects our skin’s health. Diets high in sugars, dairy, and processed foods are often linked to an increased risk of skin diseases. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2021) reported that diets high in sugar and dairy products were correlated with higher rates of acne. Conversely, incorporating fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants can help maintain your skin’s health. Moderation is key to keeping your complexion at its best. A balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, supports not only your overall health but also contributes to healthier, more resilient skin.
Skin Damage from Excessive Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure is one of the most damaging factors for your skin, leading to premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer. The Skin Cancer Foundation (2022) states that daily use of an SPF 15 or higher sunscreen reduces the risk of developing melanoma by 50%. Dermatologists recommend using sunscreen with adequate SPF, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding the sun during peak hours to protect your skin. It’s not just about preventing sunburn; prolonged UV exposure can lead to a breakdown of collagen, resulting in fine lines, wrinkles, and changes in texture. Emphasizing protection against sun damage is crucial for maintaining long-term skin health.
Smoking and Skin Disorders
Smoking is one of the worst things for your skin. It restricts blood flow, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients essential for skin health. A study by the British Journal of Dermatology (2019) revealed that smoking increases the risk of developing psoriasis, a chronic skin condition. This habit can exacerbate existing skin conditions and accelerate the aging process, leading to wrinkles and a dull complexion. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your skin’s appearance and overall health, highlighting the direct connection between smoking and skin health.
Alcohol Consumption and Skin Diseases
Excessive alcohol consumption can have a detrimental effect on your skin. Alcohol dehydrates the skin and can lead to an imbalance in hormones, both of which can contribute to skin issues. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology (2020), alcohol consumption is linked to an increased incidence of rosacea and other skin disorders. Moderation is crucial to prevent these damaging effects. Reducing alcohol intake can lead to visible improvements in skin hydration, elasticity, and overall appearance, underscoring the importance of moderation for skin health.
Lack of Sleep, Stress, and Skin Health
Chronic stress and lack of sleep are significant contributors to poor skin health. They can lead to hormonal imbalances and weaken the skin’s ability to repair itself, making it more susceptible to conditions like acne and eczema. A study in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology (2021) found that chronic stress significantly impacts skin barrier function, exacerbating various skin conditions. Prioritizing sleep and stress management is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Adequate sleep and stress reduction not only benefit your mental health but also play a vital role in keeping your skin vibrant and healthy.
Misuse of Skincare Products
Not all skincare routines are beneficial; some can be damaging. Over-exfoliating or using products with harsh chemicals can strip the skin of its natural oils. The International Journal of Dermatology (2022) warns against overuse of skin treatments like peels and mechanical exfoliation, which can lead to skin barrier disruption and increased sensitivity. It’s important to find a balance and consult with a dermatologist if you’re unsure about the products you’re using. Personalized skincare, based on individual skin type and concerns, is essential for avoiding adverse effects and achieving optimal skin health.
The Harm of Picking at Skin or Nails
Picking at your skin or nails can lead to infections and scarring. It’s a habit that should be avoided to maintain the integrity of your skin. According to the American Academy of Dermatology (2021), habitual picking can cause permanent damage to the skin, leading to scars and even infections. Seeking professional help is advised if this habit becomes compulsive. It’s important to understand that such behaviors not only affect your skin’s appearance but can also indicate underlying stress or anxiety, requiring a holistic approach to treatment and prevention.
Environmental Factors Affecting Skin Health
Environmental factors like pollution and exposure to chemicals can be harmful to your skin. These elements can lead to irritation and premature aging. A study in the Journal of Environmental Sciences (2023) found that prolonged exposure to certain pollutants can significantly increase the risk of developing dermatological conditions like eczema and acne. Protecting your skin with appropriate skincare products and minimizing exposure to harsh environments can help mitigate these risks. It’s also important to understand the role of environmental factors in skin health, especially for those living in urban areas with high pollution levels.
The Role of Photography in Skin Perception
Understanding the Impact of Photographic Techniques on Skin Appearance
Photography, especially in the era of high-resolution cameras and social media, plays a significant role in how we perceive our skin. The use of filters and editing apps has created new standards for skin appearance, often leading to unrealistic expectations. A study in the Journal of Digital Imaging (2021) highlights that certain lighting conditions and camera settings can accentuate skin imperfections or alternatively, give a misleadingly flawless appearance. This phenomenon has led to a rise in ‘Snapchat Dysmorphia,’ where individuals seek cosmetic procedures to resemble their digitally altered images.
Professionals in dermatology and psychology caution against the excessive reliance on digital enhancements, advocating for a more realistic and healthy approach to skin perception. Embracing natural skin, with its unique textures and tones, is key to fostering self-acceptance and a positive body image.
Phototherapy in Treating Skin Diseases
Exploring the Therapeutic Uses of Light in Dermatology
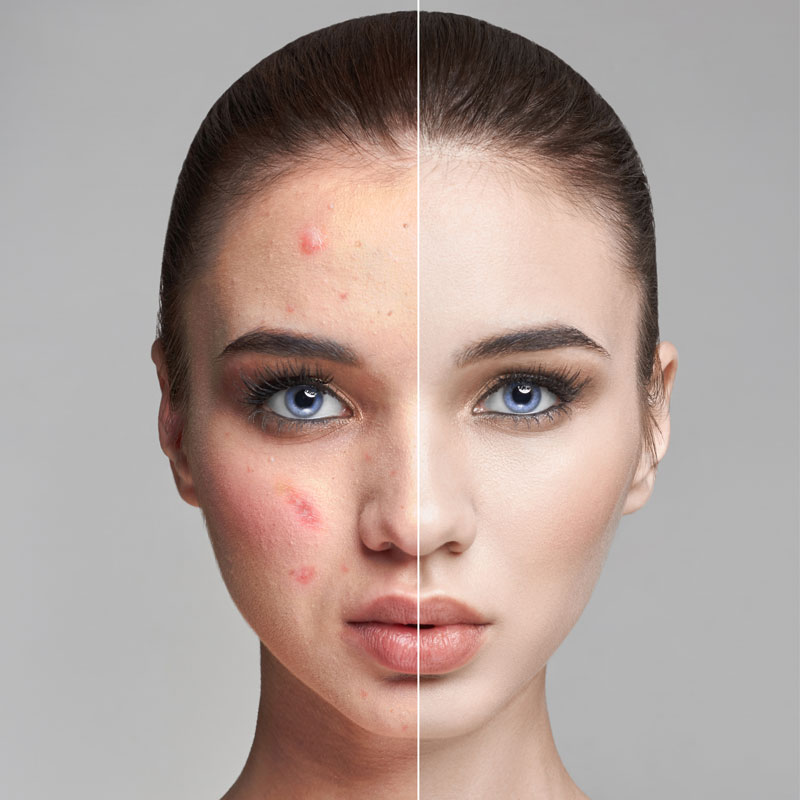
Phototherapy, the use of light to treat skin conditions, has emerged as a vital tool in dermatology. This treatment involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light, under medical supervision, to address various skin diseases. According to a review in the British Journal of Dermatology (2022), phototherapy is particularly effective in treating conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo.
There are different types of phototherapy, including UVB phototherapy, UVA phototherapy, and PUVA therapy (a combination of UVA light and a medication called psoralen). These treatments work by reducing inflammation and slowing down the overproduction of skin cells, which are common issues in many skin diseases.
Phototherapy is praised for its non-invasive nature and the ability to target specific areas of the skin without systemic side effects. However, it requires multiple sessions and must be carefully managed to avoid potential risks like skin aging or increased risk of skin cancer. Patients interested in phototherapy should consult with a dermatologist to understand the best treatment options for their specific condition.
The Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Skin Treatment
A Closer Look at UVB Light as a Dermatological Solution
UVB phototherapy has become a cornerstone treatment for several skin disorders, notably psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo. This method involves exposing the skin to the UVB spectrum of ultraviolet light, which is effective in slowing down the rapid growth of skin cells associated with these conditions.
The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (2023) reports that narrowband UVB phototherapy is particularly effective and safe for long-term use. Unlike broadband UVB, narrowband UVB emits a smaller range of ultraviolet wavelengths, focusing on those most beneficial for treatment with minimal adverse effects.
The effectiveness of UVB phototherapy lies in its ability to reduce inflammation and suppress the abnormal immune response often seen in skin diseases. Regular sessions, typically two to three times a week, are required for optimal results. Patients undergoing UVB therapy may see improvement in their skin condition within a few weeks, though results can vary based on the individual and the severity of their condition.
Dermatologists often prefer UVB phototherapy due to its targeted approach and lower risk profile compared to systemic medications. While it is generally safe, potential side effects like skin redness and increased sensitivity to sunlight are important considerations. Continuous monitoring by a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the treatment.
Conclusion: The Future of Phototherapy and At-Home Treatment Options
Navigating At-Home Phototherapy with Care and Expert Guidance
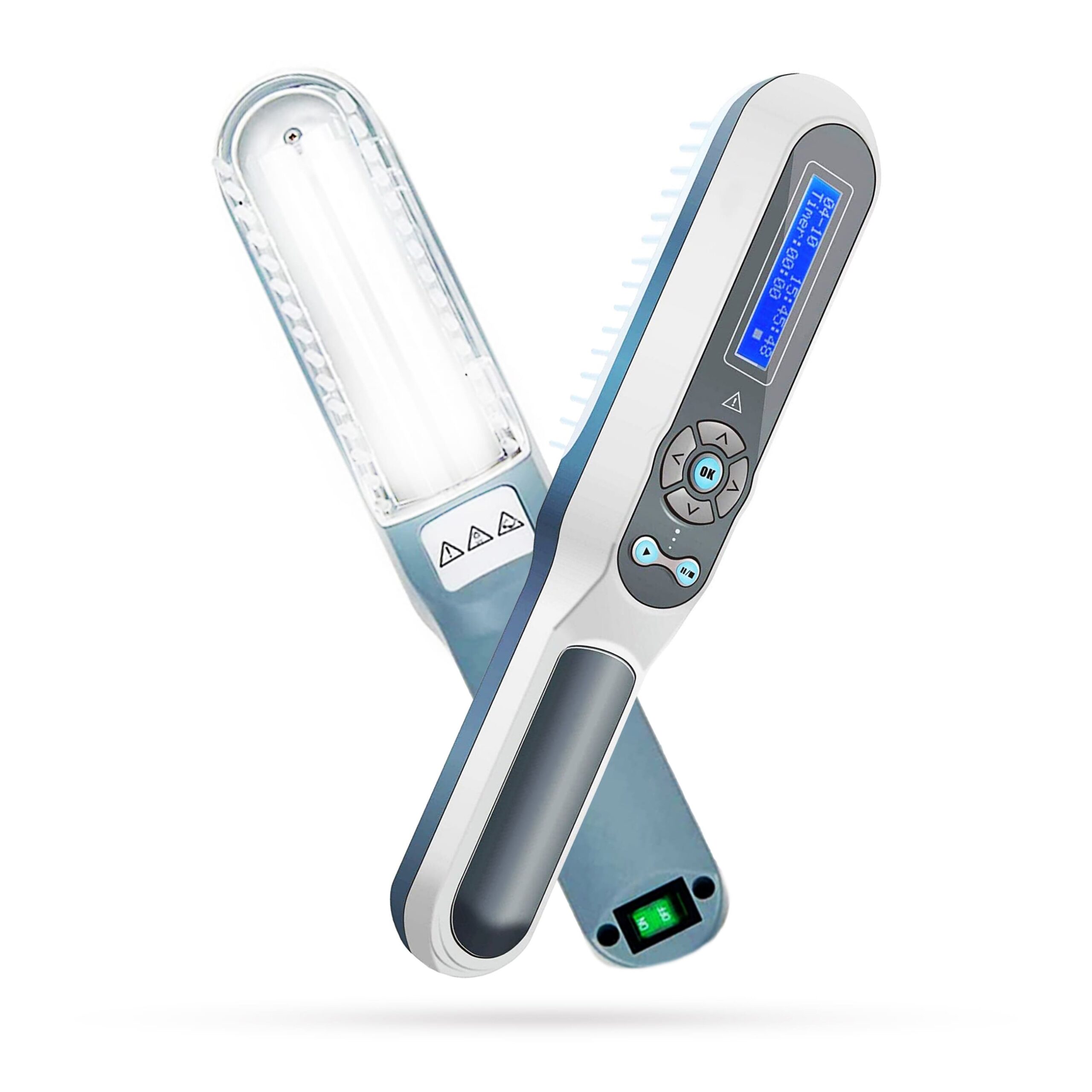
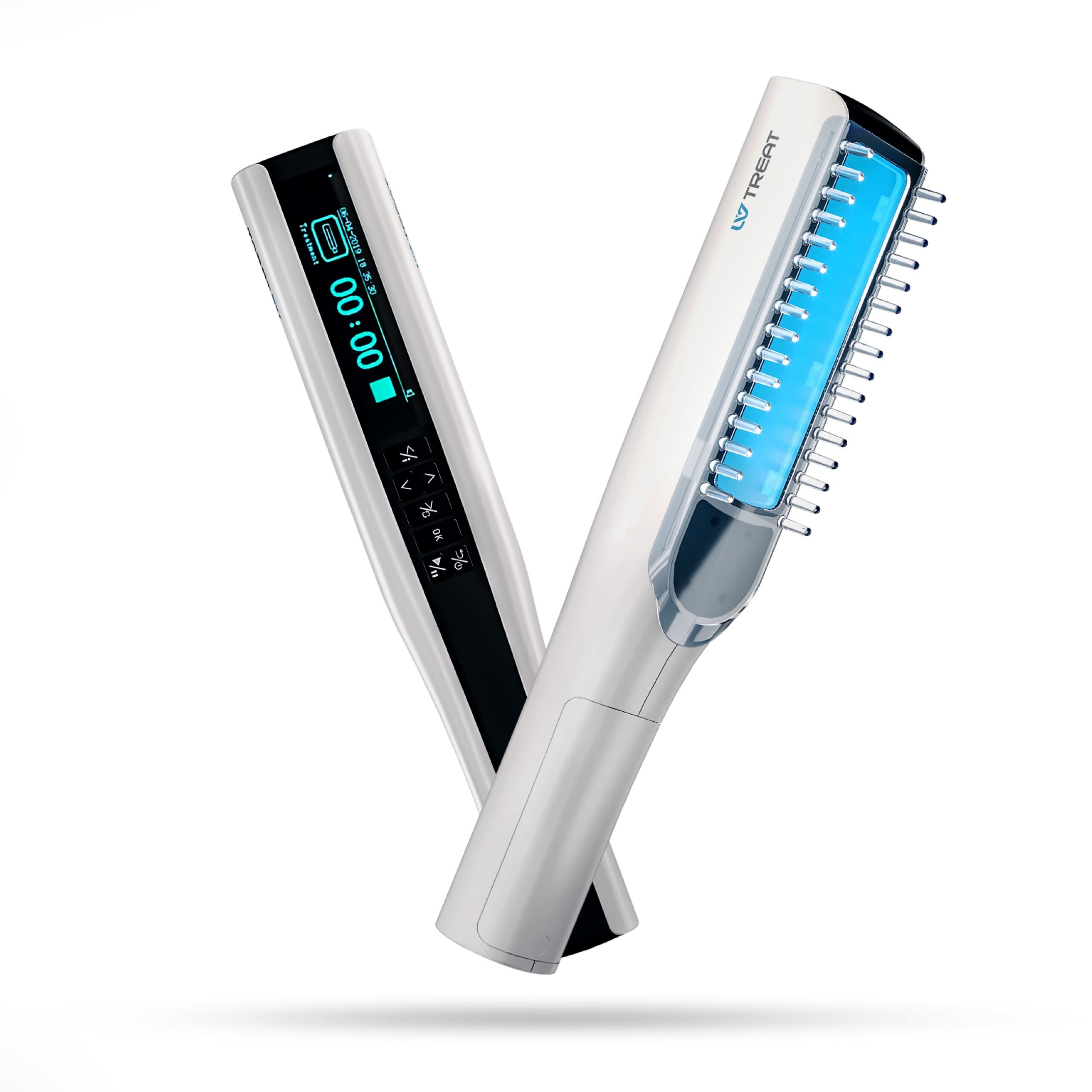
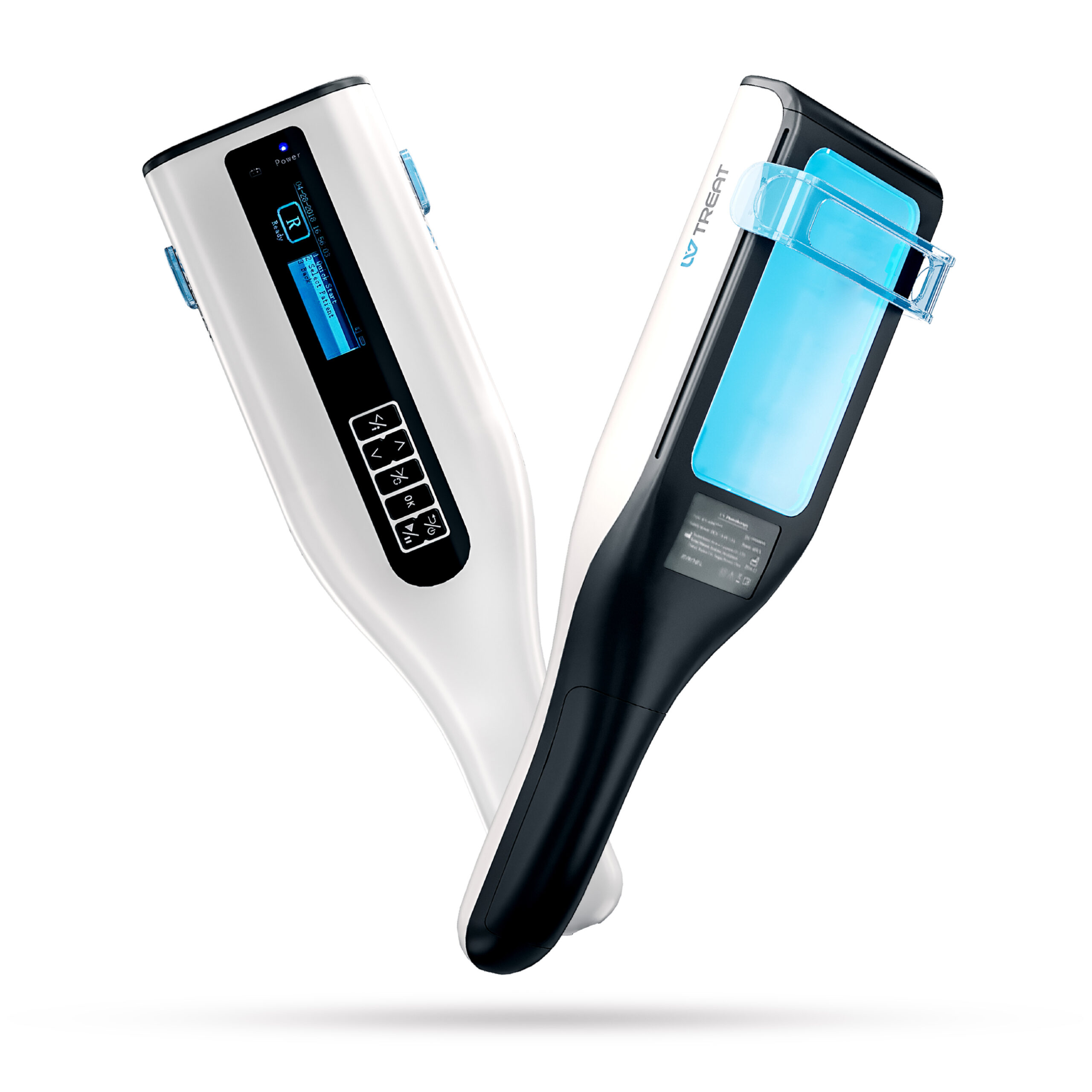
The advancement in phototherapy has paved the way for at-home treatment options, particularly with the advent of portable phototherapy devices. These devices offer a convenient and accessible means for individuals to manage their skin conditions, like psoriasis and eczema, from the comfort of their homes. Recent studies, including one in the Dermatological Therapy Journal (2023), have shown promising results in the efficacy and safety of these portable units for certain skin conditions.
However, the importance of consulting a dermatologist before starting at-home phototherapy cannot be overstated. Professional guidance is crucial in determining the suitability of the treatment, the correct usage of the device, and monitoring for any adverse reactions. Additionally, patients should be cautious and informed about the potential risks, such as overexposure and incorrect usage, which could lead to skin damage.
Furthermore, it’s beneficial for patients to engage in ongoing education and stay informed about their condition and treatment options. Reading additional materials, attending webinars, and participating in support groups can provide valuable insights and support.
In conclusion, while phototherapy, particularly UVB phototherapy, offers a promising solution for various skin conditions, the journey towards optimal skin health should always be navigated with professional advice and a well-informed understanding of the treatments available. Embracing both technological advancements and expert medical guidance is key to achieving the best outcomes in skin care and treatment.