9 Treatment Options for Eczema
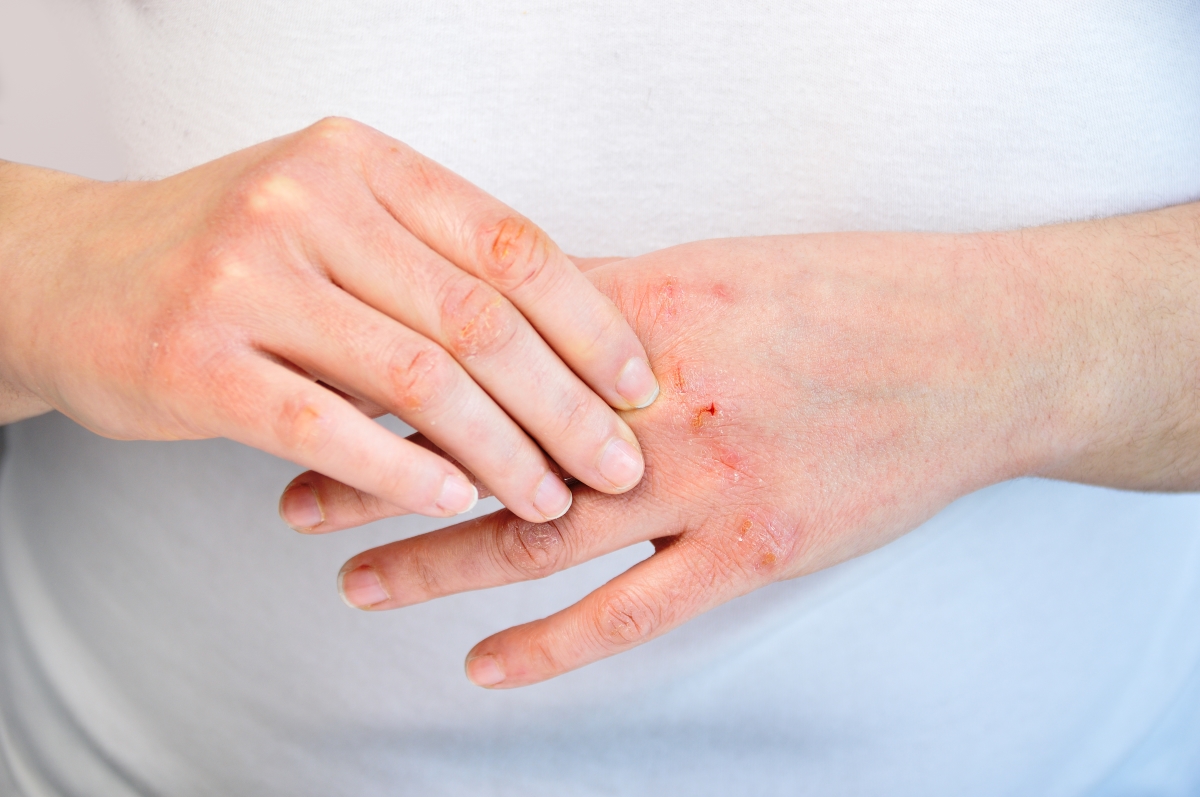
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that causes inflammation, itching, and redness. Managing eczema involves a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual’s symptoms and severity.
Here are nine effective treatment options for those suffering from eczema:
1. Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the most commonly prescribed treatments for eczema. They work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune response, leading to an improvement in symptoms such as itching and redness. The potency of topical steroids ranges from mild to very potent, and they should be used as directed by a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects like skin thinning.
2. Moisturizers
Dry skin is a hallmark of eczema, making moisturizing an essential part of treatment. Regular use of emollients helps restore the skin barrier, keeping moisture in and irritants out. Moisturizers should be applied immediately after bathing and several times throughout the day, especially on affected areas. Patients are advised to use hypoallergenic and fragrance-free products to avoid irritation.
3. Calcineurin Inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal medications that can be applied topically to treat eczema. They work by modulating the immune system to reduce inflammation and are often used for sensitive areas where corticosteroids may not be suitable. These inhibitors can be a first-line treatment for mild to moderate eczema in certain cases and provide an alternative for long-term management.
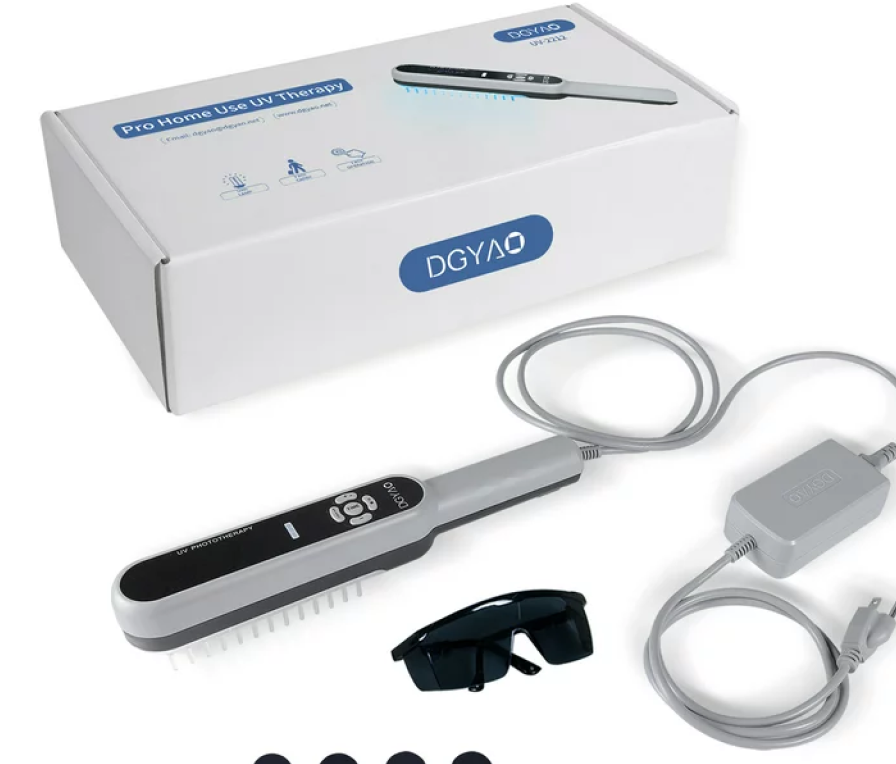
4. Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves the use of ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of eczema. This treatment is typically considered when topical treatments are insufficient. Phototherapy can help in reducing itchiness and promoting skin healing, although it requires numerous sessions under medical supervision and may not be suitable for everyone.
5. Systemic Corticosteroids
For severe eczema cases, systemic corticosteroids may be prescribed. These are taken orally or by injection, providing rapid relief of inflammation. However, due to their potential side effects—including weight gain, high blood pressure, and bone thinning—systemic corticosteroids are usually prescribed for short-term use only, under the careful guidance of a healthcare provider.
6. Biologics
Biologics are relatively new treatments for eczema and are typically reserved for moderate to severe cases unresponsive to standard therapy. These injectable medications, like dupilumab, target specific pathways in the immune system to reduce inflammation. Biologics have shown promising results, improving skin condition and quality of life for many eczema patients, with monitoring to manage possible side effects.
7. Antihistamines
Although not directly effective in treating eczema, antihistamines can help manage nighttime itching, allowing for better sleep. By blocking the action of histamine, these medications reduce itchiness and can be beneficial when used alongside primary eczema treatments. Non-sedating options are available for daytime use, while sedating antihistamines are often reserved for nighttime.
8. Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary changes and lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing eczema, especially when certain foods or environmental factors trigger flare-ups. An elimination diet can help identify and avoid allergens, while stress reduction techniques like yoga and meditation may alleviate symptoms. Additionally, wearing soft, breathable clothing and avoiding harsh soaps and detergents can minimize irritation.
9. Alternative Therapies
Many people with eczema explore complementary and alternative therapies such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and probiotics. While evidence for these treatments varies, some patients report symptom relief. It’s important to discuss any alternative treatment with a healthcare provider to ensure it complements conventional medical care effectively.
Conclusion
Optimal management of eczema relies on individualized treatment plans that incorporate one or more of these options. Through a combination of medication, skincare routine adjustments, and lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve significant symptom relief and improve their quality of life. Ongoing research continues to unveil new therapies, offering hope for even more effective interventions in the future.