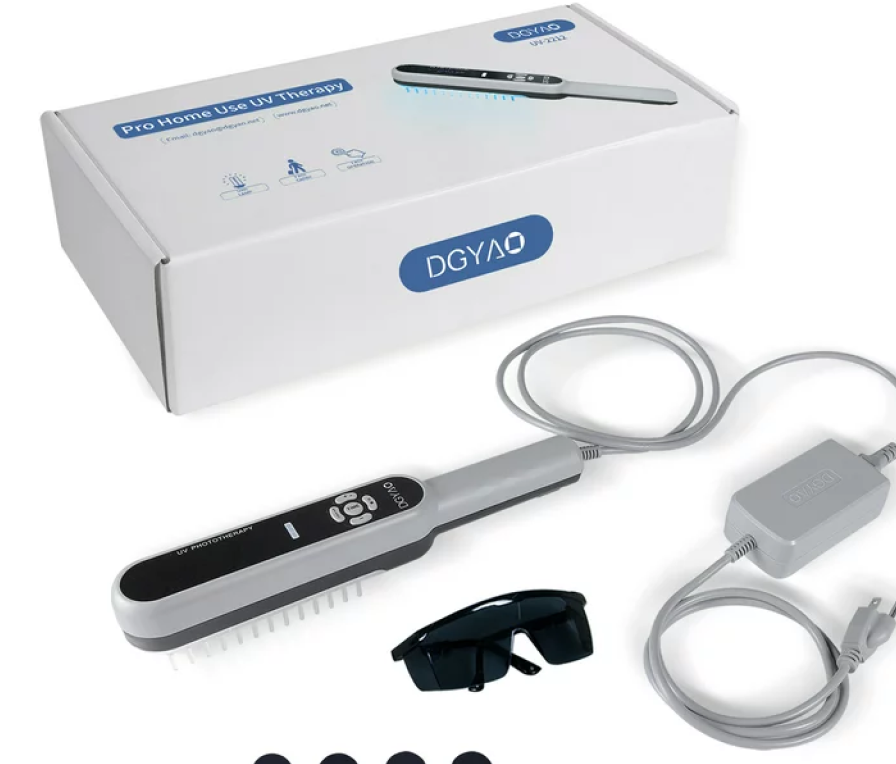
Understanding Narrowband UVB Phototherapy
Narrowband UVB phototherapy has now taken over broadband UVB phototherapy as the most common type used in the treatment of psoriasis, even for many other skin diseases like eczema, vitiligo, and vitamin D deficiency. It is cost-effective, benefiting many patients suffering from skin problems by not being able to afford expensive treatments.
To understand well why Narrowband UVB is better than broadband UVB, you first have to understand just exactly how light impacts your body and how Narrowband UVB helps in conditions like psoriasis, vitiligo, and eczema and for what reasons it is preferred in these treatments. [1]
What is UVB Phototherapy?
UVB phototherapy is a treatment that uses ultraviolet B (UVB) light to cure many skin problems. The administration of this therapy occurs by the exposure of the damaged skin to the UVB light, which slows skin cell multiplication and inflammation of the skin. Later, this suppresses DNA synthesis, decreasing the inflammation.
Narrowband UVB (311–312 nm) is favored over broadband UVB (270–350 nm) because of the shortened duration of exposure and lengthened duration of remissions. [2] In diseases ranging from psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and some forms of dermatitis, UVB phototherapy has turned out to be a common mode of treatment. Other conditions for UVB phototherapy include nodular prurigo, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, Mycosis fungoides, and Generalized pruritus, among others.
A special UVB lamp or phototherapy booth is also used for treatment, even the affected body areas can be exposed to natural sunlight in a controlled manner. Most often, UVB phototherapy treatment is explained to be safe and effective.
Types of UVB Phototherapy
There are two types of UVB phototherapy:
-
Broadband UVB
This method uses UV light in the range of (280–315 nm), type B. It’s not suitable for areas with skin folds. Conventional broadband UVB lamps emit light across a wide range of UVB wavelengths, including those causing sunburn. This can have negative effects, like increasing the risk of skin cancer and discomfort for patients.
-
Narrowband UVB (nbUVB)
This approach uses a narrower range of UVB wavelengths, specifically 311–312 nm. It can target specific areas, including skin folds. Narrow band UVB lamps emit light within a smaller, therapeutic range of wavelengths, reducing the risk of sunburn and making it potentially safer and more effective than broadband UVB. [3]
Narrowband UVB Phototherapy – The Basics
The history of Narrowband UVB Phototherapy dates back to the early 1900s when Dr. Niels Finsen and later Goeckerman studied UV light’s potential for treating skin diseases. UV phototherapy utilizes different ranges of UV light, including UVA, PUVA, and UVB. UVB phototherapy encompasses Broadband UVB (BB-UVB) and Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB), with NB-UVB being better tolerated and showing fewer side effects. [4]
NB-UVB treatment impacts inflammatory skin conditions by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting Langerhans cell activity. It suppresses the immune system’s T-cell response, leading to symptom improvement.
Narrowband UVB Phototherapy for Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects around 2.6% of the US population and varies in severity. [5] Narrow band UVB light therapy, especially, is safe and effective for many with extensive psoriasis. Topical agents like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs are typically used first for mild to moderate cases. However, severe cases may require other therapies.
UVB treatment may be unsuitable for those with very fair skin or whose condition worsens with sunlight exposure. Most patients see improvement after 12 to 24 UVB treatments, with clear skin lasting for months afterward. Further treatment may be needed if psoriasis returns.
Types of Phototherapy for Psoriasis
Phototherapy options for psoriasis include Broadband UVB (280–315 nm), Narrowband UVB (311 nm), and PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A). While PUVA is highly effective, it’s less commonly used due to side effects like nausea from psoralen ingestion. UVB phototherapy, especially Narrowband UVB, is the preferred choice for treating psoriasis. [6]
How Narrowband UVB Phototherapy Treatment Works for Psoriasis
UVB phototherapy is usually conducted at outpatient clinics, necessitating patients to commute multiple times weekly during regular business hours for their treatment sessions. This can be inconvenient. To address this, home UVB equipment was introduced in the late 1970s. [7]
Advancements in technology have led to safer home phototherapy equipment with better regulation to prevent misuse. Patients receive a thorough education on using home UVB, including treatment goals and recognizing adverse reactions.
Narrowband UVB Phototherapy for Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a common disorder with a disproportionate outcome on skin pigmentation in individuals with darker skin. Narrow-band ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) phototherapy has been one of the safe and effective options of therapies since its advent in the year 1997, and it has proven itself to be safe in the treatment of many skin diseases. [8]
The NB-UVB has been shown effective as a repigmentation stimulator in vitiligo, but yet the exact mechanism remains less well known. Other studies have found that, during NB-UVB, there is some activation in the synthesis of vitamin D3, which helps in repigmentation. It may improve the low level of vitamin D associated with vitiligo.
How Narrowband UVB Phototherapy Treatment Works for Vitiligo
UVB is very effective for vitiligo due to its immune suppression and stimulation of cytokines. Lamp TL-01 is an excellent and leading source of light for NB-UVB phototherapy, especially when using 24-48 in-office booths. It radiates at wavelengths between 310 and 315 nm, with the peak of emission at 311 nm. It filters out all unnecessary radiations that might cause severe burning or any other side effect of UV radiation.
Recent research provides good results with the NB-UVB treatment; in most of them, the patients show considerable repigmentation after months under therapy. The series of NB-UVB led to better outcomes than topical PUVA or oral PUVA in percentage and color match. [9] NB-UVB is further considered safe even in the management of childhood vitiligo, with few side effects and, in fact, providing better color matching, especially since its use has been shown to be safe even during pregnancy and lactation.
Treatment is done most frequently two times a week for 3 to 4 months; then it continues until complete repigmentation is done, which may take a few more months, especially in the case of fair skin. Narrowband UVB phototherapy is overtaking as one of the leading ways of treating vitiligo, with continued advancements in phototherapy methods. [10]
Narrowband UVB Phototherapy for Eczema
Eczema, aka atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and cracked skin. Phototherapy is used in eczema or atopic dermatitis (AD) to suppress the Th2 immune response, improve the skin barrier, and reduce skin infections. [11]
Current guidelines recommend Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) as a second-line therapy for children and adults with acute or chronic AD that doesn’t respond to topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators. Several retrospective studies have shown a significant reduction in Eczema severity in children with NB-UVB treatment.
Systematic reviews consistently support Narrowband UVB Phototherapy as an effective form of phototherapy for Eczema compared to other light-based treatments. [12]
Narrowband UVB Phototherapy for Vitamin D Deficiency
In summer, the major source of vitamin D is sunshine, which activates ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. Global insufficiency of VD controls body functions with levels of calcium. Its deficiency has been associated with skeletal and extraskeletal diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The optimum VD level for nonskeletal effects is still doubtful, but the most important marker is 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]. [13]
Previous studies demonstrated that phototherapy, in turn, narrowband UVB, increased the synthesis of vitamin D. UV radiation may also be an intervening factor in the mechanism for influencing folate levels in the body. Therefore, it can be said that for patients having a low level of 25(OH)D, low-dose narrowband UVB greatly increases their vitamin D status. [14]
Home-Based UVB Phototherapy
While NB-UVB is commonly administered in clinics, home-based treatment is more seen as a safe and productive modality for certain patients. Studies approve the efficacy of home-based phototherapy for conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo. [15]
Most dermatologists expect that narrowband UVB phototherapy will soon replace broad-spectrum UVB, particularly in the home setting.
Home Phototherapy Units
The choice of UVB phototherapy panel is a decision that should be made by the patient and their clinician. Even though the risks of home phototherapy overall are low and consist of skin reactions, such as erythema and burns, this treatment should be done solely among reliable patients.
Patients should be informed about treatment aims, such as the fact that flares may occur from time to time, prior to the initiation of home phototherapy. Compulsory safeguards include the strict following of recommendations; for example, one should wear goggles and cover the most sensitive areas.
Summing Up!
Over time, narrowband UVB phototherapy has emerged as an effective treatment for various conditions like vitiligo, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and others. Home-based phototherapy (HBPT) emerged as a viable option despite a decline in office-based treatments.
HBPT, delivered through lamps, booths, or hand/foot devices, ensures treatment compliance and offers cost-effective healthcare utilization. Patients should know how to manage adverse reactions and the importance of regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.