Published on February 23, 2024
NB-UVB & Afamelanotide in Treating Vitiligo
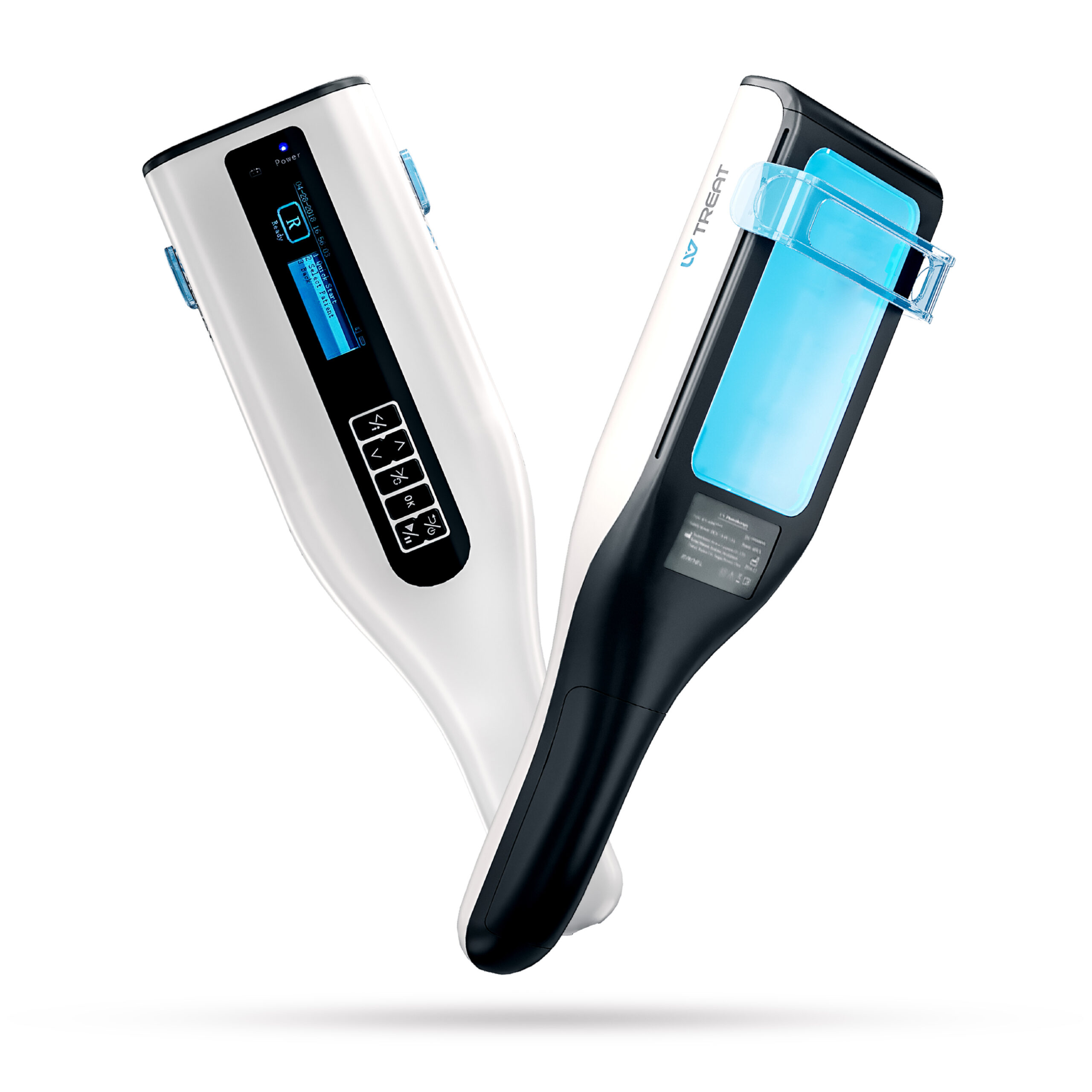
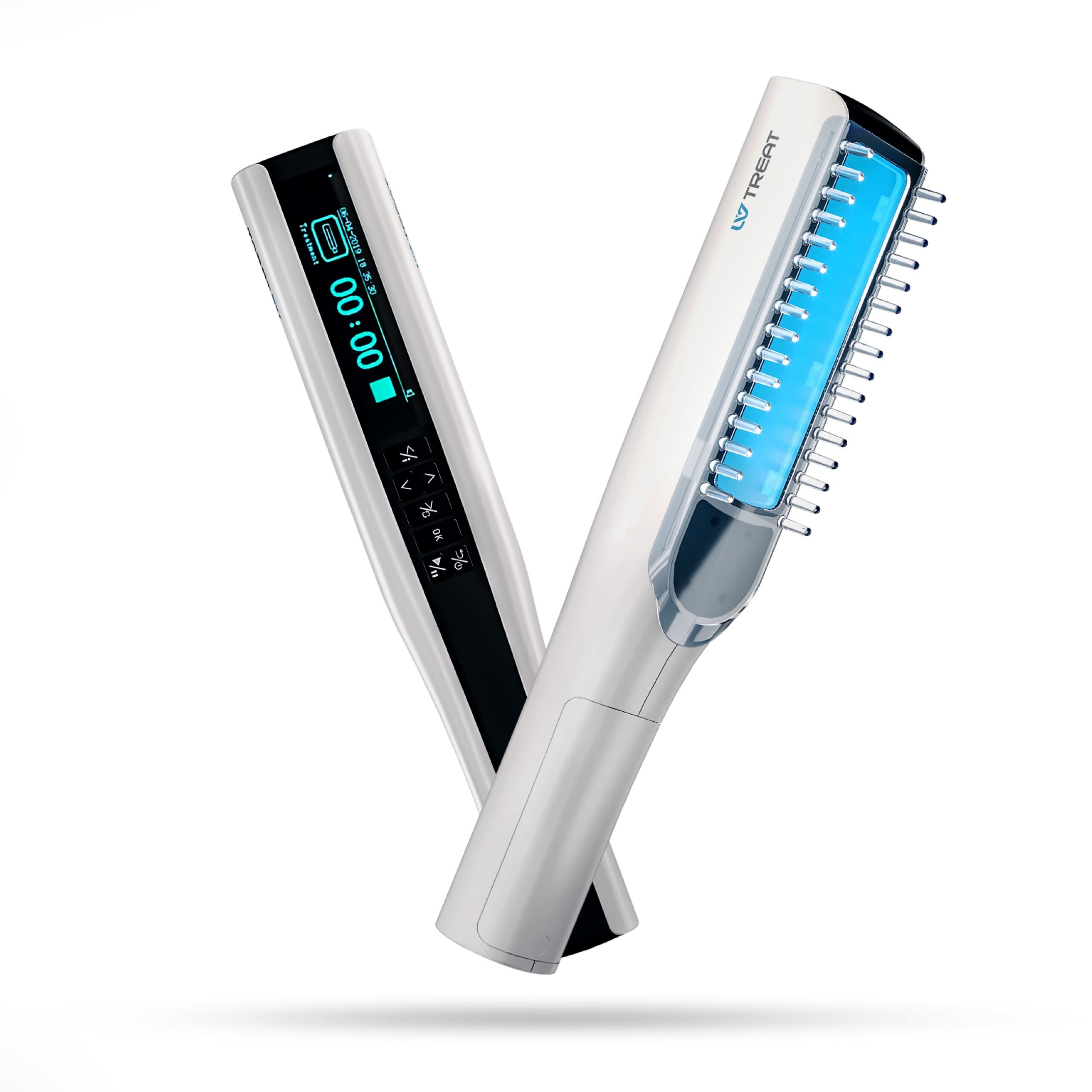
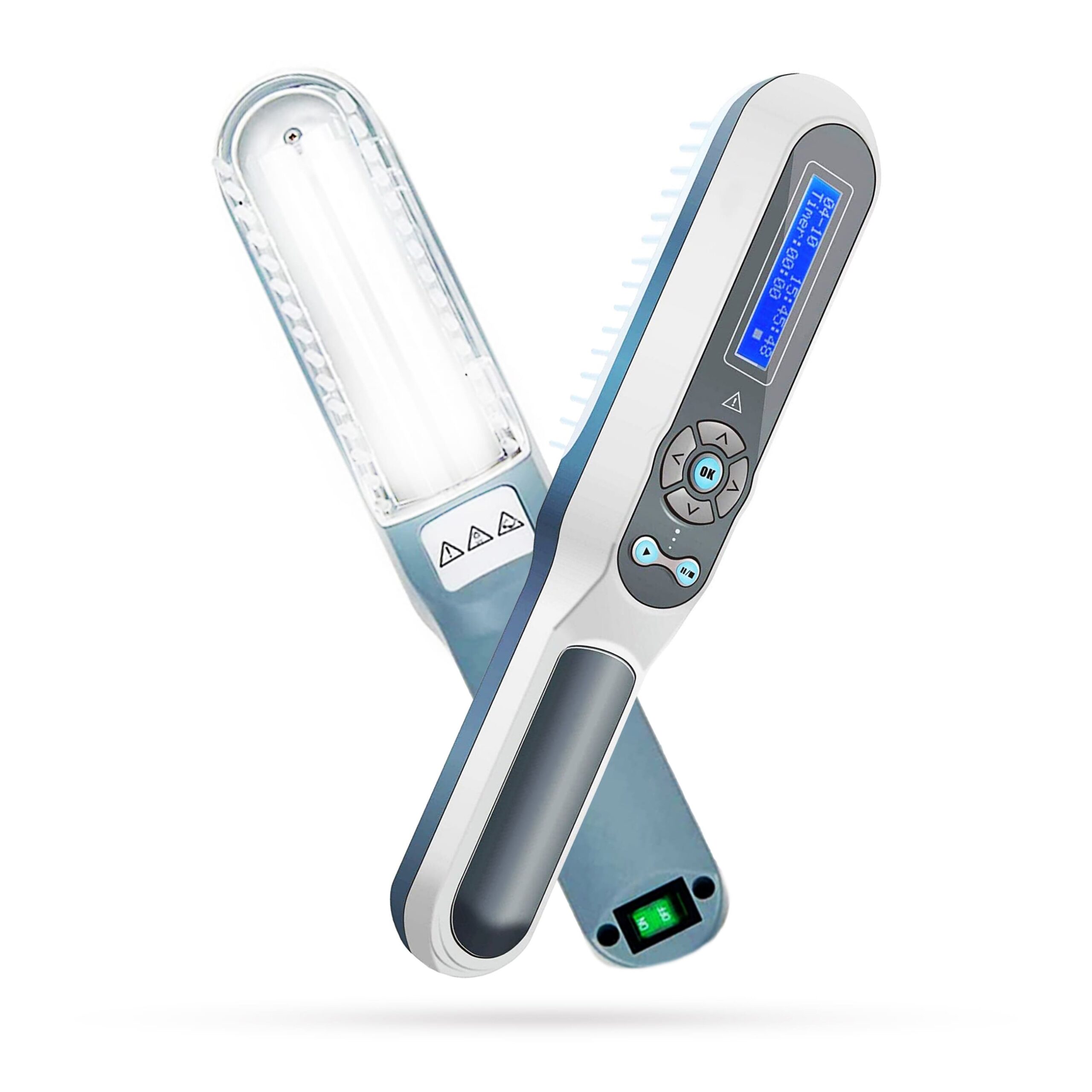
Grimes et al (2013) noted that many recent studies have demonstrated defects in the melanocortin system in patients with vitiligo, including decreased circulating and lesional skin levels of α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). Afamelanotide is a potent and longer-lasting synthetic analog of naturally occurring α-MSH. These investigators described the preliminary results of 4 patients with generalized vitiligo who developed re-pigmentation using afamelanotide in combination with narrowband UV-B (NB-UV-B) phototherapy. Patients were treated 3 times weekly with NB-UV-B and starting in the 2nd month received a series of 4 monthly implants containing 16 mg of afamelanotide. Afamelanotide induced faster and deeper re-pigmentation in each case. All patients experienced follicular and confluent areas of re-pigmentation within 2 days to 4 weeks after the initial implant, which progressed significantly throughout treatment. All patients experienced diffuse hyper-pigmentation. The authors proposed that afamelanotide represents a novel and potentially effective treatment for vitiligo. The combined therapy of NB-UV-B and afamelanotide appears to promote melanoblast differentiation, proliferation, and eumelanogenesis.
References
- https://www.aetna.com/cpb/medical/data/400_499/0422.html
- Grimes PE, Hamzavi I, Lebwohl M, et al. The efficacy of afamelanotide and narrowband UV-B phototherapy for repigmentation of vitiligo. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149(1):68-73.